Complete Guide to Modern Project Management & Collaboration Tools
- project-management
- collaboration
- slack
- trello
- github
- coderabbit
- productivity
- team-workflow
Complete Guide to Modern Project Management & Collaboration Tools
Effective project management requires the right combination of tools and practices. This guide explores how to leverage Slack, Trello, GitHub, and CodeRabbit to build a seamless collaborative workflow for your development team.
Slack: Your Team's Communication Hub
Slack transforms team communication from scattered emails into organized, searchable conversations. Here's how to maximize its potential for project management:
Setting Up Your Workspace
Start by creating dedicated channels for different aspects of your project. Use naming conventions like #project-frontend, #project-backend, and #project-general to keep conversations organized. Public channels encourage transparency, while private channels work well for sensitive discussions like HR matters or financial planning.
Communication Best Practices
The key to effective Slack usage is threading. When someone posts a question or update, reply in a thread rather than posting new messages. This keeps the main channel clean and makes conversations easy to follow. Use the pin feature to highlight important messages like meeting notes, deployment schedules, or critical decisions that team members need to reference frequently.
Mentions are powerful but should be used thoughtfully. @channel notifies everyone in a channel and should be reserved for truly urgent matters. @here notifies only active users, making it better for time-sensitive but non-critical updates. For routine questions, mention specific people who can help.
Integration Power
Connect Slack to your other tools to centralize notifications. Integrate GitHub to receive pull request updates, Trello to get card movement notifications, and calendar tools for meeting reminders. This creates a single source of truth where team members can stay informed without constantly switching between applications.
Managing Information Overload
Create a culture of using status updates. Encourage team members to set custom statuses like "In a meeting" or "Deep work - slow to respond." Set up do-not-disturb schedules to protect focus time. Use the saved items feature to bookmark important messages for later review rather than trying to remember everything.
Trello: Visual Project Organization
Trello's board-and-card system provides an intuitive way to track work visually. It's particularly effective for teams that think in terms of workflows and stages.
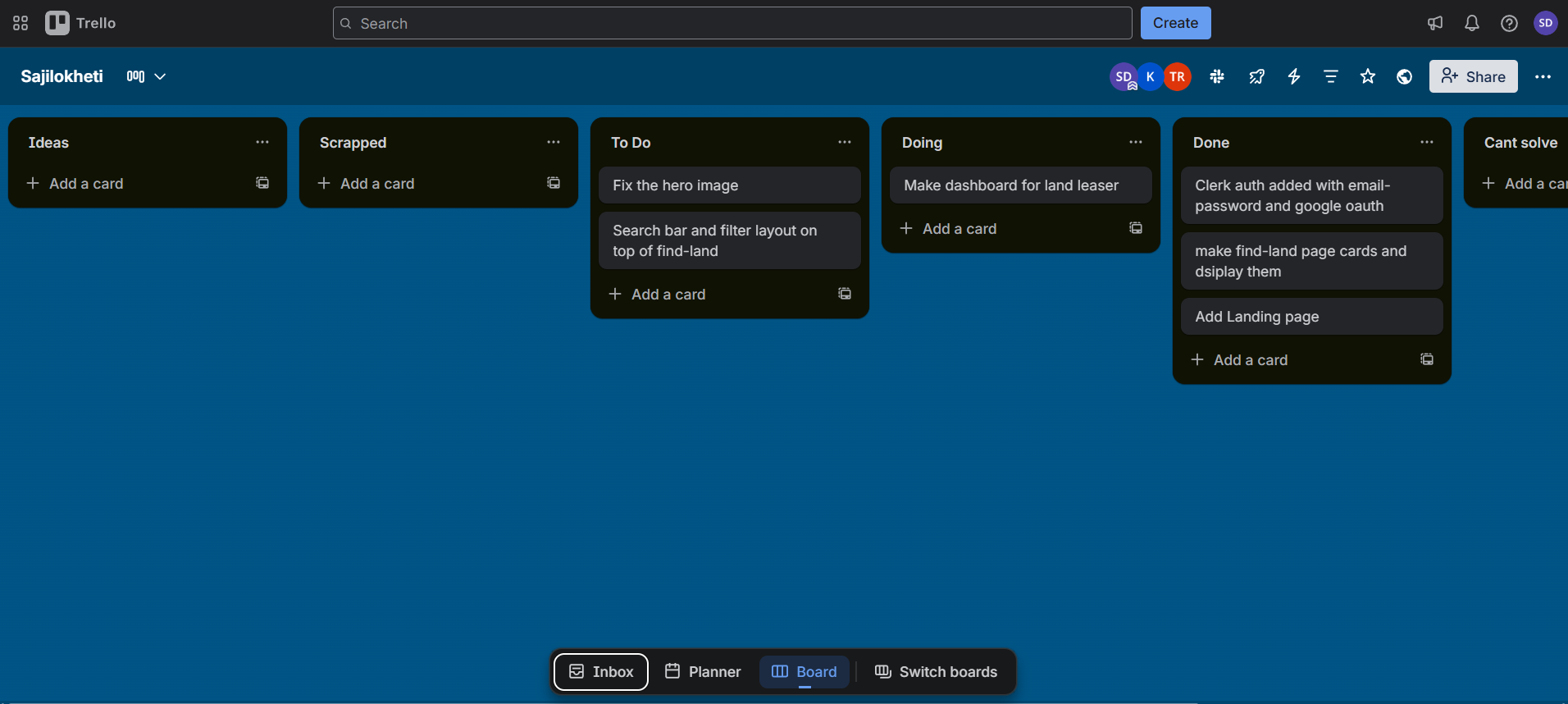
Board Structure for Development Teams
Create boards that mirror your workflow. A typical development board might include lists like Backlog, To Do, In Progress, Code Review, Testing, and Done. Each card represents a task or feature, moving from left to right as work progresses.
For larger projects, consider multiple boards: one for overall project planning, another for sprint execution, and perhaps a third for bug tracking. Use Trello's workspace feature to keep related boards together and manageable.
Card Organization Strategies
Every card should tell a complete story. Write clear titles that explain what needs to be done, not just project jargon. In the description, include acceptance criteria, relevant links, design mockups, and any context someone needs to complete the work. This prevents confusion and reduces back-and-forth questions.
Labels add powerful categorization. Use color-coded labels for priority levels, work types (feature, bug, technical debt), or team ownership (frontend, backend, DevOps). This allows team members to quickly scan the board and understand the landscape at a glance.
Collaboration Features
Assign team members to cards to clarify ownership. Add due dates to create accountability and help with timeline planning. Use checklists within cards to break down complex tasks into smaller steps, making progress visible and work less overwhelming.
The comment section on each card becomes a mini-conversation thread. Use it to ask questions, provide updates, or share relevant information. This keeps all context in one place rather than buried in email or chat.
Power-Ups for Enhanced Functionality
Trello's Power-Ups extend functionality significantly. The Calendar Power-Up visualizes deadlines across your board. The GitHub Power-Up attaches pull requests directly to cards, linking planning with execution. Custom Fields let you add structured data like story points, time estimates, or custom statuses.
GitHub: Code Collaboration Central
GitHub does more than store code—it's a complete collaboration platform for development teams. Understanding its project management features transforms how teams work together.
Repository Organization
Structure your repositories thoughtfully from the start. Use a clear README that explains what the project does, how to set it up, and how to contribute. Include a CONTRIBUTING.md file that outlines your team's development process, coding standards, and pull request expectations.
Leverage GitHub's built-in project boards for issue tracking. These integrate directly with your code, creating tight connections between planning and implementation. Create issue templates that guide team members to provide necessary information when reporting bugs or proposing features.
Branching Strategy
Adopt a branching strategy that matches your team's workflow. Git Flow works well for projects with scheduled releases, using main, develop, and feature branches. GitHub Flow offers a simpler alternative: create a branch for each feature, submit a pull request, review, merge to main, and deploy.
Name branches descriptively using patterns like feature/user-authentication or bugfix/login-validation. This makes the purpose immediately clear and helps with organizing work.
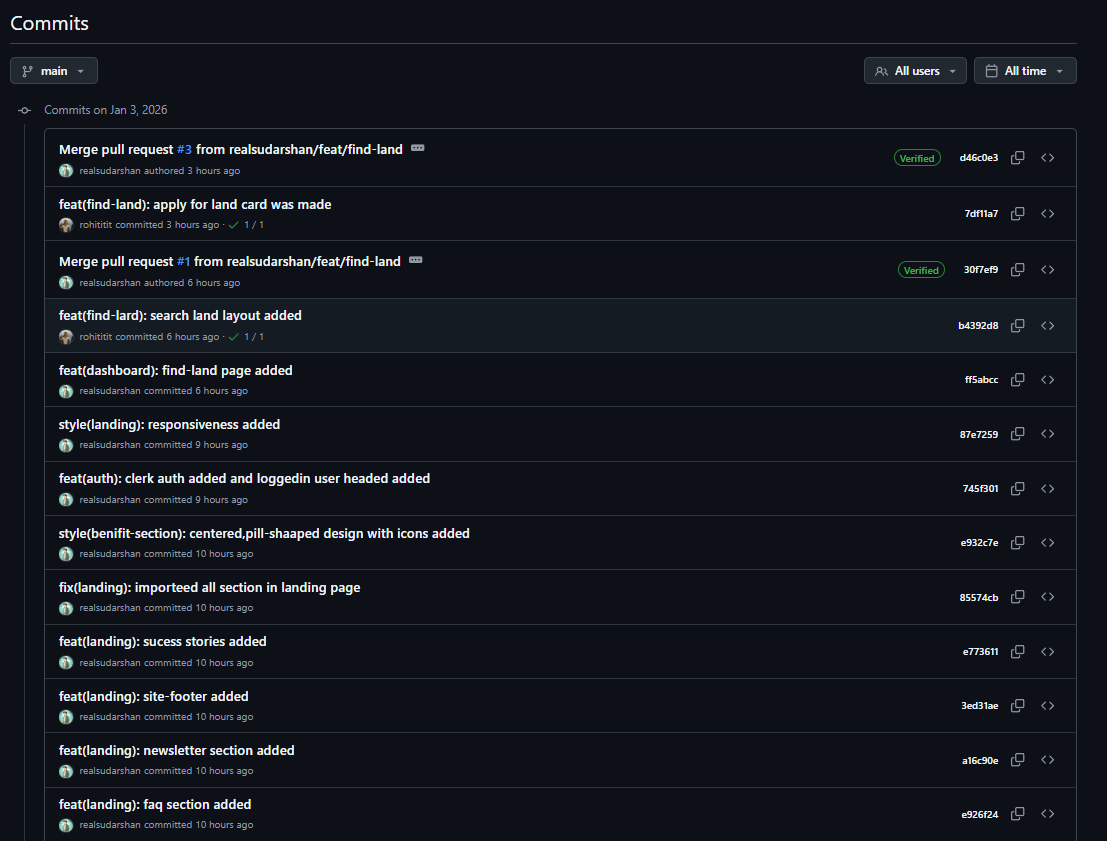
Pull Request Excellence
Pull requests are where code collaboration happens. Write descriptive titles and detailed descriptions explaining what changed and why. Link to related issues using keywords like "Closes #123" to automatically close issues when the PR merges.
Request reviews from team members with relevant expertise. Use GitHub's review features to leave comments on specific lines of code. Approve when ready, request changes when needed, and engage in constructive dialogue to improve the code.
Keep pull requests focused and reasonably sized. Smaller PRs are easier to review thoroughly and merge faster. If a feature requires many changes, consider breaking it into multiple PRs that each add incremental value.
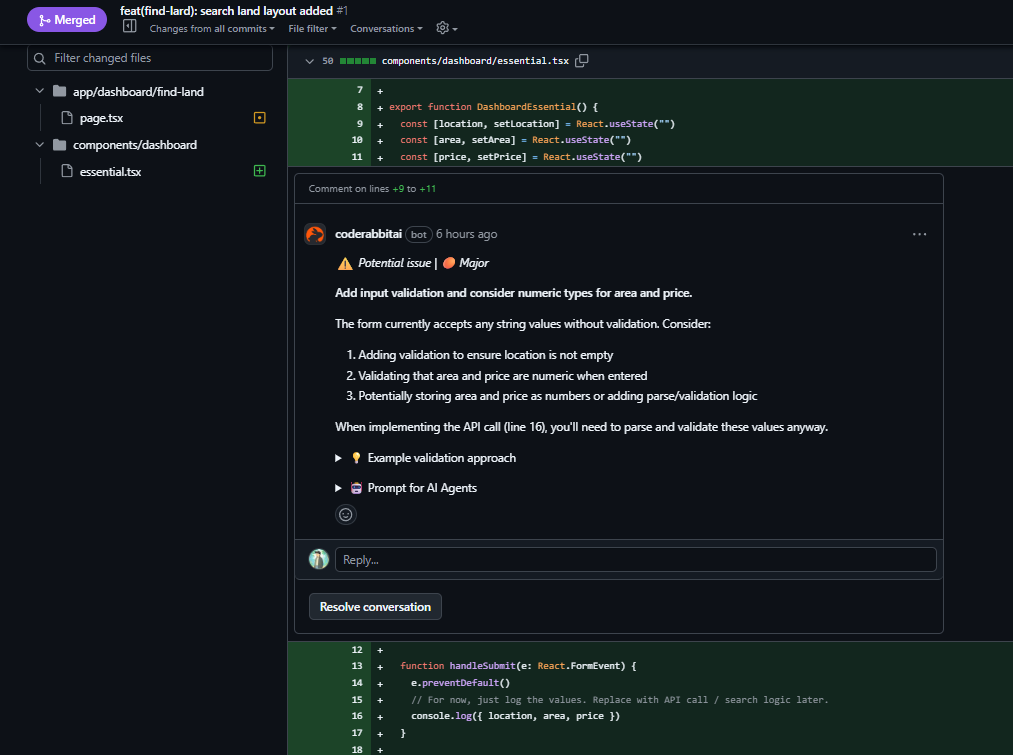
Issues and Project Tracking
Use GitHub Issues as your single source of truth for work items. Write clear titles, detailed descriptions, and add appropriate labels. Milestones group related issues, providing a way to track progress toward larger goals like version releases.
GitHub Projects (the newer beta version with table and board views) offers sophisticated project management directly in GitHub. Create custom fields, automate workflows, and visualize work across multiple repositories. This keeps planning close to implementation without requiring external tools.
Branch Protection and Code Quality
Configure branch protection rules to enforce your quality standards. Require pull request reviews before merging, ensure status checks pass, and prevent force pushes to important branches. These guardrails prevent mistakes and maintain code quality.
CodeRabbit: AI-Powered Code Review
CodeRabbit represents the next evolution in code review, using AI to augment human reviewers and catch issues before they reach production.
How CodeRabbit Works
Once integrated with your GitHub repository, CodeRabbit automatically reviews every pull request. It analyzes code changes, identifies potential issues, suggests improvements, and provides context-aware feedback. Unlike simple linters, CodeRabbit understands the broader context of your changes and how they fit into the overall codebase.
Benefits for Code Review
CodeRabbit catches common issues immediately: potential bugs, security vulnerabilities, performance concerns, and code style inconsistencies. This frees human reviewers to focus on higher-level concerns like architecture decisions, business logic, and design patterns.
The AI learns from your team's patterns and preferences over time. It understands your coding conventions and can enforce consistency across the codebase. This is particularly valuable for larger teams where maintaining standards becomes challenging.
Integration Best Practices
Configure CodeRabbit to match your team's needs. Set it to automatically comment on pull requests with findings, but configure the severity levels appropriately. Not every suggestion needs to block merging—use it as a guide rather than a gatekeeper.
Encourage team members to engage with CodeRabbit's suggestions. Sometimes it's right, sometimes it provides a different perspective worth considering, and sometimes it's wrong. Treat it as an additional team member offering input, not an infallible authority.
Combine CodeRabbit with human review rather than replacing it. AI excels at catching patterns and common mistakes, while humans excel at understanding business context and making nuanced decisions. Together, they create thorough, efficient code review.
Measuring Impact
Track metrics to understand CodeRabbit's value. Monitor how many issues it catches before human review, how it affects review time, and whether it reduces bugs in production. This data helps justify the investment and identify areas for adjustment.
Best Practices for Collaborative Development
Bringing these tools together requires intentional practices that foster genuine collaboration and productivity.
Establish Clear Communication Norms
Define when to use each communication channel. Slack works well for quick questions and real-time coordination. GitHub comments belong with code-specific discussions. Trello cards document decisions and requirements. Email (if used) handles formal communications or external stakeholders.
Create response time expectations. Not everything needs immediate attention. Clarify what constitutes urgent versus important, and respect people's focus time by defaulting to asynchronous communication unless real-time discussion is truly necessary.
Documentation as a Habit
Documentation isn't an afterthought—it's part of the work. Update README files as projects evolve. Write meaningful commit messages that explain why changes were made, not just what changed. Document architectural decisions in GitHub discussions or wiki pages.
Good documentation reduces interruptions. When information is easily findable, team members can self-serve instead of asking the same questions repeatedly. This respect for others' time compounds into significant productivity gains.
Regular Synchronization Points
Schedule regular check-ins that match your development rhythm. Daily standups keep everyone aligned on immediate work. Sprint planning sessions ensure the team understands upcoming priorities. Retrospectives create space to improve processes continuously.
Keep meetings focused and valuable. Share written updates beforehand so meeting time focuses on discussion, not status reporting. End each meeting with clear action items and owners.
Transparent Progress Tracking
Make work visible across the team. Keep Trello boards updated so anyone can see project status at a glance. Move GitHub issues through their lifecycle promptly. Update Slack channels with meaningful progress updates, not just "working on it."
Visibility enables help. When someone is blocked or falling behind, transparent tracking allows team members to offer assistance before problems escalate. It also builds trust—everyone can see that work is happening and progressing.
Code Review Culture
Build a culture where code review is collaborative, not combative. Frame feedback constructively, focusing on the code rather than the person. Assume good intent and ask questions when something seems off rather than making accusations.
Review promptly. Sitting on pull requests creates bottlenecks and slows everyone down. Aim to provide initial feedback within a few hours during working time. If a thorough review will take longer, leave a quick acknowledgment so the author knows it's on your radar.
Be specific in reviews. Instead of "this could be better," explain what concerns you and potentially suggest alternatives. Provide context for your feedback so the author understands the reasoning, not just the prescription.
Automation and Integration
Automate repetitive tasks to free mental energy for creative work. Set up continuous integration to run tests automatically on every push. Configure automatic deployments for branches or environments. Use GitHub Actions or similar tools to enforce code quality standards automatically.
Integrate tools to reduce context switching. Connect GitHub to Slack for PR notifications. Link Trello cards to GitHub issues. Set up webhooks to keep systems synchronized. The less manual coordination required, the more time available for actual work.
Managing Technical Debt
Address technical debt proactively rather than letting it accumulate. Create Trello cards or GitHub issues for known debt, and allocate time in each sprint to address some of it. This prevents the gradual degradation that makes codebases increasingly difficult to work with.
Make technical debt visible alongside feature work so stakeholders understand the tradeoffs. Sometimes shipping a feature with some debt is the right business decision, but it should be a conscious choice rather than an accident.
Onboarding and Knowledge Sharing
Use your tools to create smooth onboarding experiences. Maintain up-to-date setup documentation in GitHub. Create Trello boards specifically for onboarding that guide new team members through learning the codebase and processes. Record important discussions and decisions so new people can understand the context behind current states.
Encourage knowledge sharing through pairing, code review, and documentation. No single person should be the only one who understands a critical system. Distribute knowledge to reduce risk and empower the entire team.
Bringing It All Together
The magic happens when these tools work in concert. Here's what a typical workflow might look like:
A new feature is discussed in a Slack thread, where the team aligns on the general approach. Someone creates a Trello card capturing the requirements, acceptance criteria, and relevant design links. That Trello card links to a GitHub issue for tracking the technical implementation.
A developer creates a feature branch in GitHub and begins work. They commit regularly with clear messages describing their progress. When ready, they open a pull request that references the GitHub issue. CodeRabbit immediately reviews the code and provides initial feedback.
The developer addresses CodeRabbit's suggestions and requests review from teammates. Reviewers receive a Slack notification via the GitHub integration. They review the code, leave comments, and approve the changes. The PR merges, automatically closing the GitHub issue.
The Trello card moves to Done, and a Slack notification informs the team that the feature is ready for testing. Throughout this process, all discussions remain searchable and attached to the relevant work items, creating a rich history that helps future debugging and feature development.
Conclusion
Effective collaboration isn't about having the fanciest tools—it's about using the right tools intentionally and building practices that respect people's time and attention. Slack streamlines communication, Trello provides visual organization, GitHub enables code collaboration, and CodeRabbit enhances code quality through AI assistance.
The key is integration and consistency. Choose tools that work together, establish clear practices for using them, and continuously refine your approach based on what works for your team. Start with the basics, build good habits, and layer in sophistication as your team's needs evolve.
Great collaboration multiplies the impact of individual effort. When information flows freely, when progress is visible, and when the friction of coordination disappears, teams achieve remarkable things. These tools, used well, create that environment.